关于本章
本章讨论”computer algebra“即”计算代数“。
在学习back propagation的时候,查阅了 如何直观地解释 backpropagation 算法? - YE Y的回答 - 知乎 ,其中提及了“计算代数”,查询了一下,在计算机科学中是有这种学科的:Computer algebra,下面是wikipedia Computer algebra 。
wikipedia Computer algebra
In mathematics and computer science, computer algebra, also called symbolic computation or algebraic computation, is a scientific area that refers to the study and development of algorithms and software for manipulating mathematical expressions and other mathematical objects.
NOTE: 需要注意的是,在一些场合常常使用symbolic computation
NOTE: 关于symbol,参见
Relation-structure-computation\Symbol章节
Computer algebra VS scientific computing
Although computer algebra could be considered a subfield of scientific computing, they are generally considered as distinct fields because scientific computing is usually based on numerical computation with approximate floating point numbers, while symbolic computation emphasizes exact computation with expressions containing variables that have no given value and are manipulated as symbols.
Computer algebra systems
Software applications that perform symbolic calculations are called computer algebra systems.
NOTE: TensorFlow其实可以看做是一个computer algebra system
Computer science aspects
NOTE: 这是作为software engineer的人需要关注的
Data representation
It is common, in computer algebra, to emphasize exact computation with exactly represented data. Such an exact representation implies that, even when the size of the output is small, the intermediate data generated during a computation may grow in an unpredictable way. This behavior is called expression swell(膨胀). To obviate this problem, various methods are used in the representation of the data, as well as in the algorithms that manipulate them.
NOTE: 原文这一节所讨论的是: 如何来使用计算机语言来表示Numbers、Expressions?
Numbers
NOTE: 本节所讨论的是如何来表示number?
Expressions
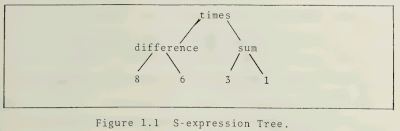
Representation of the expression
(8-6)*(3+1)as a Lisp tree, from a 1985 Master's Thesis.[7]NOTE: expression能够方便的使用tree来进行表示,然后转换为三地址码。
Except for numbers and variables, every mathematical expression may be viewed as the symbol of an operator followed by a sequence of operands. In computer algebra software, the expressions are usually represented in this way. This representation is very flexible, and many things that seem not to be mathematical expressions at first glance, may be represented and manipulated as such. For example, an equation is an expression with “=” as an operator, a matrix may be represented as an expression with “matrix” as an operator and its rows as operands.
Even programs may be considered and represented as expressions with operator “procedure” and, at least, two operands, the list of parameters and the body, which is itself an expression with “body” as an operator and a sequence of instructions as operands.
Conversely, any mathematical expression may be viewed as a program. For example, the expression a + b may be viewed as a program for the addition, with a and b as parameters. Executing this program consists in evaluating the expression for given values of a and b; if they do not have any value—that is they are indeterminates—, the result of the evaluation is simply its input.
This process of delayed evaluation is fundamental in computer algebra. For example, the operator “=” of the equations is also, in most computer algebra systems, the name of the program of the equality test: normally, the evaluation of an equation results in an equation, but, when an equality test is needed,—either explicitly asked by the user through an “evaluation to a Boolean” command, or automatically started by the system in the case of a test inside a program—then the evaluation to a boolean 0 or 1 is executed.
As the size of the operands of an expression is unpredictable and may change during a working session, the sequence of the operands is usually represented as a sequence of either pointers (like in Macsyma) or entries in a hash table (like in Maple).
Simplification
NOTE: 对expression进行simplification是非常重要的,重要能够大大地降低运算的复杂性。
This simplification is normally done through rewriting rules. There are several classes of rewriting rules that have to be considered. The simplest consists in the rewriting rules that always reduce the size of the expression, like E − E → 0 or sin(0) → 0. They are systematically applied in computer algebra systems.
Implementation of computer algebra: symbolic programming
本节描述如何实现computer algebra,目前最常采用的一种方式是symbolic programming,在工程programming-language的Theory\Programming-paradigm\Symbolic-programming章节对它进行了详细介绍。
在software engineering中,我们常常需要以通用的方式来描述一个数学计算,比如:
1) 如何描述computation graph
2) 在量化交易中,自定义**基差**计算公式
3) ......
在这类应用中,往往存在着两个阶段:
1) 构建阶段
使用symbol来构建math expression,往往需要使用domain-specifier language,比如直接使用math language。
2) Evaluation阶段
然后对这些symbol进行赋值,然后对math expression进行evaluate,从而得到最终的结果。
Examples
下面是一些具体的实现:
SymPy
SymPy is a Python library for symbolic mathematics. It aims to become a full-featured computer algebra system (CAS) while keeping the code as simple as possible in order to be comprehensible and easily extensible. SymPy is written entirely in Python.
ArashPartow exprtk
Deep learning
Deep learning中,我们需要构建computational graph,computational graph就是典型的symbolic mathematics。目前大多数deep learning implementation,都支持symbolic programming。
Expression template
Expression template是C++ TMP中的一种重要trick,参见C-family-language\C++\Idiom\TMP\Expression-Template。
Wolfram Language
参见wikipedia Wolfram Language:
It emphasizes symbolic computation, functional programming, and rule-based programming[8] and can employ arbitrary structures and data.[8] It is the programming language of the mathematical symbolic computation program Mathematica.[9]
Symbolic programming VS imperative programming in Symbolic mathematics
关于这个主题,参见工程machine-learning的Programming\Programming-paradigm\Symbolic-and-imperative章节。