Write a program to print all permutations of a given string
问题描述
A permutation, also called an “arrangement number” or “order,” is a rearrangement of the elements of an ordered list S into a one-to-one correspondence with S itself. A string of length n has n! permutation. Source: Mathword(http://mathworld.wolfram.com/Permutation.html)
Below are the permutations of string ABC. ABC ACB BAC BCA CBA CAB
算法
Here is a solution that is used as a basis in backtracking.
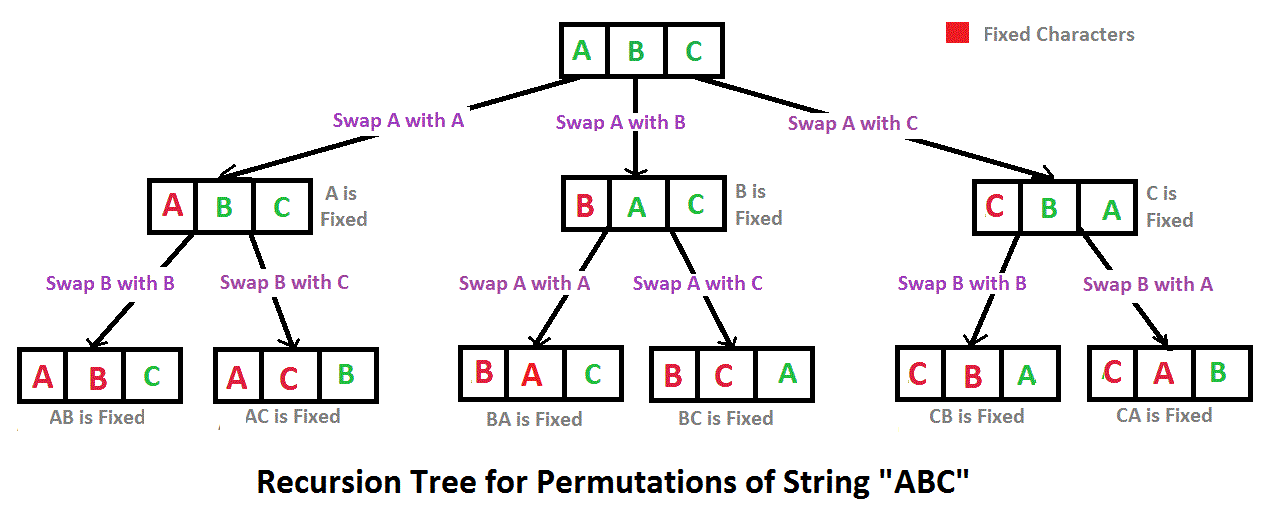
SUMMARY : 上述图已经非常好地展示了backtracking算法的调用过程,结合下面的代码来看的话,对上面的recursion tree进行先序遍历就是下面的函数的调用过程;该函数的目的是生成所有的permutation的,即它需要穷举;
生成permutation的过程可以简述为:
- 从n个元素中挑选出一个来作为第0个元素
- 从n-1个元素中挑选出一个来作为第1个元素
- 从n-2个元素中挑选出一个来作为第2个元素
- ...
- 从2个元素中挑选出一个来作为第n-2个元素
- 从1个元素中挑选出一个来作为第n-1个元素
显然上述过程是一个递归的过程,上述过程如果使用图形化来展示的话,其实和上面的recursion tree是完美对应的:
- recursion tree的第一层节点,对应了从n(n=3)个元素中挑选出一个来作为第0个元素
- recursion tree的第二层节点,对应了从n-1(n-1=2)个元素中挑选出一个来作为第1个元素
recursion tree中的每一条路径就对应了一个组合;
所以,共有n \times (n-1) \times (n-2) \times \ldots \times 2 \times 1种排列,n \times (n-1) \times (n-2) \times \ldots \times 2 \times 1是和上述recursion tree完美对应的:
- 第一个元素选定为
A,对应了第一棵子树,显然共有n棵类似这样的子树,所以是n \times
由于我们的backtrack算法目的是**穷举**,所以在第一个元素选定为A后,还需要去尝试第一个元素选定为B的情况,还需要去产生第一个元素选定为C的情况;以此类推,在第二个元素选定为A后,还需要去尝试第二个元素选定为B的情况,还需要去产生第二个元素选定为C的情况;所以我们需要回溯,即回退到上一层的状态,这样上一层就能够尝试另外一种情况了;其实这就是backtracking算法的核心思想所在了;
对上述递归数进行先序遍历就对应了递归函数实际的执行过程,需要注意的是,当第一次由上到下经过一条边的时候,执行swap函数,当第二次由下到上经过该边的时候,执行方向相反的swap函数;这也说明递归调用是深度优先地遍历。
那上述过程如何使用递归函数来进行实现呢?这就是一个程序员需要考虑的问题了。对于这个问题,我们常常考虑的是使用backtracking算法:
C++
// C++ program to print all
// permutations with duplicates allowed
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function to print permutations of string
// This function takes three parameters:
// 1. String
// 2. Starting index of the string
// 3. Ending index of the string.
void permute(string a, int l, int r)
{
// Base case
if (l == r)
cout<<a<<endl;
else
{
// Permutations made
for (int i = l; i <= r; i++)
{
// Swapping done
swap(a[l], a[i]);
// Recursion called
permute(a, l+1, r);
//backtrack
swap(a[l], a[i]);
}
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
string str = "ABC";
int n = str.size();
permute(str, 0, n-1);
return 0;
}
// This is code is contributed by rathbhupendra
C
// C program to print all permutations with duplicates allowed
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
/* Function to swap values at two pointers */
void swap(char *x, char *y)
{
char temp;
temp = *x;
*x = *y;
*y = temp;
}
/* Function to print permutations of string
This function takes three parameters:
1. String
2. Starting index of the string
3. Ending index of the string. */
void permute(char *a, int l, int r)
{
int i;
if (l == r)
printf("%s\n", a);
else
{
for (i = l; i <= r; i++)
{
swap((a+l), (a+i));
permute(a, l+1, r);
swap((a+l), (a+i)); //backtrack
}
}
}
/* Driver program to test above functions */
int main()
{
char str[] = "ABC";
int n = strlen(str);
permute(str, 0, n-1);
return 0;
}