Graph、tree and list
进化:从list到tree,从tree到graph;
退化:graph退化为tree,tree退化为list;
树和图都可能退化成链,所以其实链也具备部分tree和graph的关系。反过来说其实就是树和图是链的泛化。
其实可以看到,很多基于graph、tree的结构或设计都有对应的线性版本,比如 Merkle tree,它的线性版本就是Hash chain。
从relation的角度来进行分析
参见 Relation-structure-computation\Model 章节。
|
Trees |
Graphs |
| Path |
Tree is special form of graph i.e. minimally connected graph and having only one path between any two vertices. |
In graph there can be more than one path i.e. graph can have uni-directional or bi-directional paths (edges) between nodes |
| Loops |
Tree is a special case of graph having no loops, no circuits and no self-loops. |
Graph can have loops, circuits as well as can have self-loops. |
| Root Node |
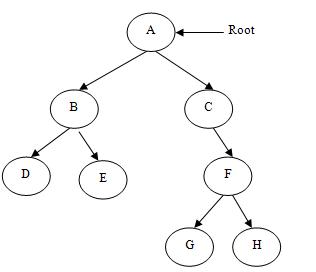
In tree there is exactly one root node and every child have only one parent. |
In graph there is no such concept of root node.
NOTE: In graph, a node can be specified as the root node. |
| Parent Child relationship |
In trees, there is parent child relationship so flow can be there with direction top to bottom or vice versa. |
In Graph there is no such parent child relationship. |
| Complexity |
Trees are less complex then graphs as having no cycles, no self-loops and still connected. |
Graphs are more complex in compare to trees as it can have cycles, loops etc |
| Types of Traversal |
Tree traversal is a kind of special case of traversal of graph. Tree is traversed in Pre-Order, In-Order and Post-Order (all three in DFS or in BFS algorithm) |
Graph is traversed by DFS: Depth First Search and in BFS : Breadth First Search algorithm |
| Connection Rules |
In trees, there are many rules / restrictions for making connections between nodes through edges. |
In graphs no such rules/ restrictions are there for connecting the nodes through edges. |
| DAG |
Trees come in the category of DAG : Directed Acyclic Graphs is a kind of directed graph that have no cycles. |
Graph can be Cyclic or Acyclic. |
| Different Types |
Different types of trees are : Binary Tree , Binary Search Tree, AVL tree, Heaps. |
There are mainly two types of Graphs : Directed and Undirected graphs. |
| Applications |
Tree applications : sorting and searching like Tree Traversal & Binary Search. |
Graph applications : Coloring of maps, in OR (PERT & CPM), algorithms, Graph coloring, job scheduling, etc. |
| No. of edges |
Tree always has n-1 edges. |
In Graph, no. of edges depend on the graph. |
| Model |
Tree is a hierarchical model. |
Graph is a network model. |
| Figure |
 |
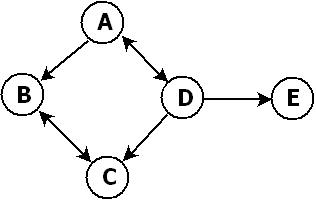 |
树中每个节点都只能有一个父节点,图中一个节点可以有多个父节点。
离散数学中对tree的定义:
a tree is a connected undirected graph with no simple circuits
这蕴含着
an undirected graph is a tree if and only if there is a unique simple path between any two of its vertices
如果两个点之间有多条path的话,则必然就形成了circuit了

