std::transform
cppreference std::transform
Parameters
unary_op
unary operation function object that will be applied.
NOTE: function object的概念在
C++\Language-reference\Functions\Function.md中进行了介绍。
The signature of the function should be equivalent to the following:
Ret fun(const Type &a);
The signature does not need to have const &.
NOTE: 上述函数原型有
const &,但是又说实际可用不包含,如何实现?
Notes
std::transform does not guarantee in-order application of unary_op or binary_op. To apply a function to a sequence in-order or to apply a function that modifies the elements of a sequence, use std::for_each
NOTE: 哪些情况下是不保证in-order的?
Example
#include <algorithm>
#include <cctype>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
int main()
{
std::string s("hello");
// 转换为大写
std::transform(s.begin(), s.end(), s.begin(),
[](unsigned char c) -> unsigned char { return std::toupper(c);});
// 获得对应的ASCII值
std::vector<std::size_t> ordinals;
std::transform(s.begin(), s.end(), std::back_inserter(ordinals),
[](unsigned char c) -> std::size_t { return c;});
std::cout << s << ':';
for (auto ord : ordinals)
{
std::cout << ' ' << ord;
}
// 相加
// C++11写法
std::transform(ordinals.cbegin(), ordinals.cend(), ordinals.cbegin(),
ordinals.begin(), std::plus<std::size_t> { });
// C++17写法
// 支持 Class template argument deduction (CTAD) (since C++17) ,参见 https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/language/class_template_argument_deduction
// std::transform(ordinals.cbegin(), ordinals.cend(), ordinals.cbegin(),
// ordinals.begin(), std::plus<> { });
std::cout << '\n';
for (auto ord : ordinals)
{
std::cout << ord << ' ';
}
std::cout << '\n';
}
// g++ --std=c++11 test.cpp
fluentcpp std::transform, a central algorithm
std::transform on a range
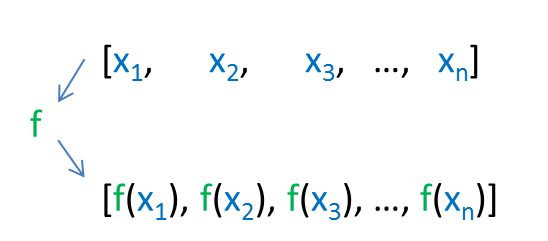
std::transform on two ranges
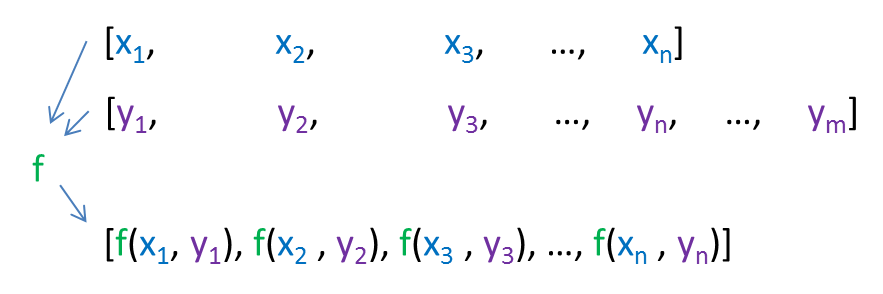
#include <algorithm>
#include <cctype>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<int> numbers1 = { 1, 5, 42, 7, 8 };
vector<int> numbers2 = { 10, 7, 4, 2, 2 };
vector<int> results;
std::transform(numbers1.begin(), numbers1.end(),
numbers2.begin(),
std::back_inserter(results),
[](int i, int j) { return i+j;});
}
// g++ --std=c++11 test.cpp