Aspect-oriented programming
Aspect-oriented programming即面向切面编程,后面简称AOP。AOP是一种编程思想,它让我们使用aspect来进行抽象。
wikipedia Aspect-oriented programming
wikipedia Cross-cutting concern
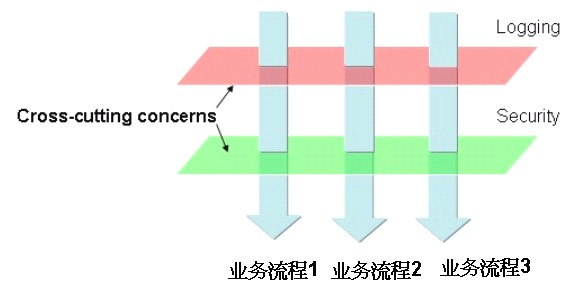
NOTE: 横切关注点,在下面我们可以看到,cross-cutting concern对应的就是一个layer。
wikipedia Separation of concerns
Spring AOP
Java spring框架充分运用了AOP,下面是对此的说明:
1) tutorialspoint AOP with Spring Framework
2) What is aspect-oriented programming? # A :
Copied from Spring in Action
AOP is often defined as a technique that promotes separation of concerns in a software system. Systems are composed of several components, each responsible for a specific piece of functionality. But often these components also carry additional responsibilities beyond their core functionality. System services such as logging, transaction management, and security often find their way into components whose core responsibilities is something else. These system services are commonly referred to as cross-cutting concerns because they tend to cut across multiple components in a system.
Good article
cnblogs C++11实现一个轻量级的AOP框架 :
AOP(Aspect-Oriented Programming,面向方面编程),可以解决面向对象编程中的一些问题,是OOP的一种有益补充。面向对象编程中的继承是一种从上而下的关系,不适合定义从左到右的**横向关系**,如果继承体系中的很多无关联的对象都有一些**公共行为**,这些公共行为可能分散在不同的组件、不同的对象之中,通过继承方式提取这些公共行为就不太合适了。使用AOP还有一种情况是为了提高程序的可维护性,AOP将程序的非核心逻辑都“横切”出来,将**非核心逻辑**和**核心逻辑**分离,使我们能集中精力在**核心逻辑**上,例如图1所示的这种情况。
stackoverflow What is aspect-oriented programming? # A:
AOP addresses the problem of cross-cutting concerns, which would be any kind of code that is repeated in different methods and can't normally be completely refactored into its own module, like with logging or verification. So, with AOP you can leave that stuff out of the main code and define it vertically(垂直) like so:
function mainProgram()
{
var x = foo();
doSomethingWith(x);
return x;
}
aspect logging
{
// 之前
before (mainProgram is called):
{
log.Write("entering mainProgram");
}
// 之后
after (mainProgram is called):
{
log.Write( "exiting mainProgram with return value of "
+ mainProgram.returnValue);
}
}
aspect verification
{
before (doSomethingWith is called):
{
if (doSomethingWith.arguments[0] == null)
{
throw NullArgumentException();
}
if (!doSomethingWith.caller.isAuthenticated)
{
throw Securityexception();
}
}
}
And then an aspect-weaver is used to compile the code into this:
function mainProgram()
{
log.Write("entering mainProgram");
var x = foo();
if (x == null) throw NullArgumentException();
if (!mainProgramIsAuthenticated()) throw Securityexception();
doSomethingWith(x);
log.Write("exiting mainProgram with return value of "+ x);
return x;
}
AOP and layer
在 refactoring.guru Command 中,对AOP和layer进行了说明:
Good software design is often based on the principle of separation of concerns, which usually results in breaking an app into layers. The most common example: a layer for the graphical user interface(GUI) and another layer for the business logic. The GUI layer is responsible for rendering a beautiful picture on the screen, capturing any input and showing results of what the user and the app are doing. However, when it comes to doing something important, like calculating the trajectory(轨道) of the moon or composing an annual report, the GUI layer delegates the work to the underlying layer of business logic.
AOP中的一个cross-cutting concern对应的就是一个layer。
Application
1、公共(common)操作,比如:
a) 每次执行某些操作,都需要记录日志、校验权限、更新统计信息
b) ......
2、Python的标准库中,大量的使用aspect-oriented programming。
3、AOP是非常适合于 流程型(flow of handling request) 的architecture,比如 message processing system
OOP VS AOP
参见Theory\Programming-paradigm\Abstraction\Abstraction-in-programming-language。
Implementation
不同的programming language对AOP的实现方式是不同的:
| language | 章节 |
|---|---|
| Python | Python\Paradigm\AOP |
| C++ | C++\Idiom\AOP |