Harvard architecture
wikipedia Harvard architecture
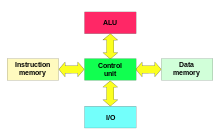
The Harvard architecture is a computer architecture with physically separate storage and signal pathways for instructions and data. The term originated from the Harvard Mark I relay-based computer, which stored instructions on punched tape (24 bits wide) and data in electro-mechanical counters. These early machines had data storage entirely contained within the central processing unit, and provided no access to the instruction storage as data. Programs needed to be loaded by an operator; the processor could not initialize itself.
TRANSLATION : 哈佛体系结构是一种计算机体系结构,它为指令和数据分别提供了物理上独立的存储和信号通路。这个术语起源于基于哈佛Mark I中继的计算机,它将指令存储在穿孔带(24位宽)上,并将数据存储在机电计数器中。这些早期机器的数据存储完全包含在中央处理单元中,不提供对指令存储作为数据的访问。操作人员需要加载的程序;处理器无法初始化自己。
SUMMARY : 第一句话就就点明了Harvard architecture与Von Neumann architecture最大的差别,它在于如何对待instruction 和 data;Von Neumann architecture并不区分instruction和data,它将它们都视为data;而Harvard architecture则严格区分两者;
Today, most processors implement such separate signal pathways for performance reasons, but actually implement a modified Harvard architecture, so they can support tasks like loading a program from disk storage as data and then executing it.
Harvard architecture